Diabetes - diagnosis & treatment
Diagnosis of diabetes disease
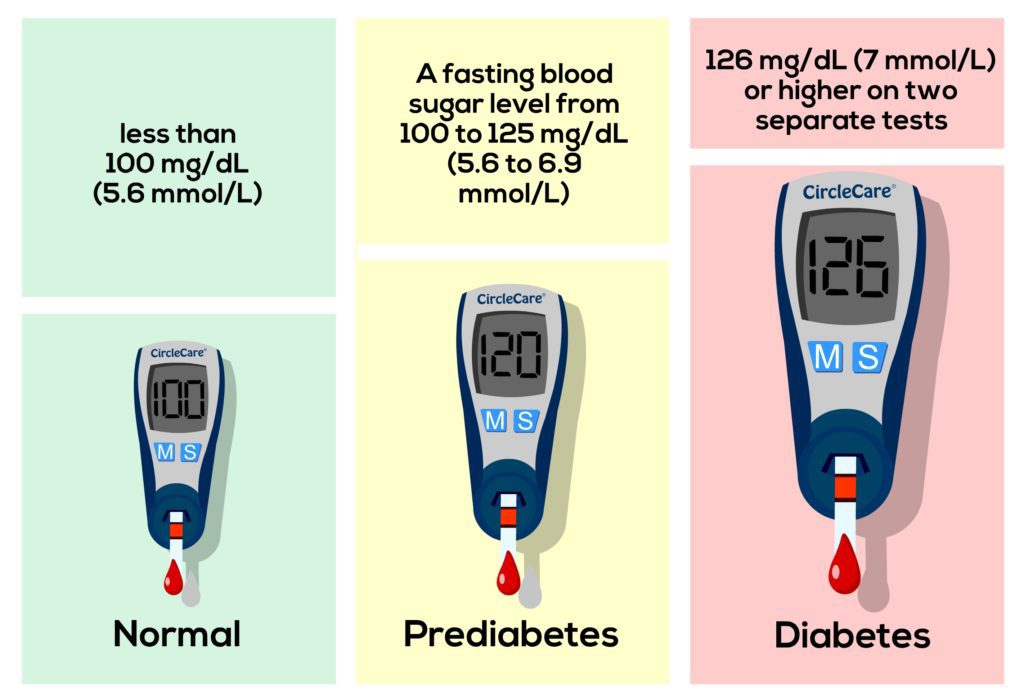
Diabetes is diagnosed by performing glucose tests to know the blood sugar levels of the patient.Fasting Plasma Glucose Test - This test is performed to know the blood glucose at least after the 8 hours of without eating, it helps in detecting diabetes and pre-diabetes in the person.
Plasma Glucose Result (mg/dL) | Diagnosis |
99 and below | Normal (impaired fasting glucose) |
100 to 125 | Prediabetes |
126 and above | Diabetes |
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) - This test is performed to know the blood glucose at least after the 8 hours of without eating and two hours after drinking glucose-containing beverage, that helps in detecting diabetes and pre-diabetes in the person.
2-Hour Plasma Glucose Result (mg/dL) | Diagnosis |
139 and below | Normal |
140 to 199 | Prediabetes |
200 and above | Diabetes |
Random plasma glucose test - this test is recommended to know blood sugar levels without regard to the last meal taken by the patient. If a patient found with 200 mg/dL or more, plus presence of the following symptoms, can mean that patient have diabetes:
Increased urination
Incensed thirst
Unknown weight loss
Treatment
Monitoring blood sugar - Maintaining normal glucose levels is a must for people with diabetes. People who receive insulin therapy also may choose to monitor their blood sugar levels with the help of continuous glucose monitors. People with type 2 diabetes who don't take insulin generally check their blood sugar much less frequently.
Insulin - Insulin therapy is needed for type - 1 diabetes, to survive. It is also given to type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes patients. But depending on the patient conditions doctors recommend types of insulin like rapid-acting insulin, long-acting insulin and intermediate options.
Oral or other medication - Medications stimulate pancreas to produce and release more insulin, others inhibit the production and release of glucose from the liver, which means those who need less insulin to transport sugar into their body cells.
Transplantation - For a type -1 diabetes a pancreas transplant may be an option, this don't recommend insulin therapy after transplant. Islet transplants are being studied as well, but they are not successful always.
Bariatric surgery - According to recent studies treatment for type 2 diabetes, people with type 2 diabetes who are obese and have a body mass index higher than 35 may benefit from this type of surgery.
Non pharmaceutical treatment includes:
- Healthy eating - Maintain a proper diet on more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains, foods that are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fat and calories and reduce taking saturated fats, refined carbohydrates and sweets.
Physical activity - Exercise lowers blood sugar level by moving sugar into patients cells, where it's used for energy. Exercise also increases patient sensitivity to insulin, which means their body needs less insulin to transport sugar to their body cells.